Fuse
A fuse is a device that stops the flow of current once a current threshold is reached. In electronic devices these are usually used for overcurrent protection. In microeletronic devices these are typically used for configuration.
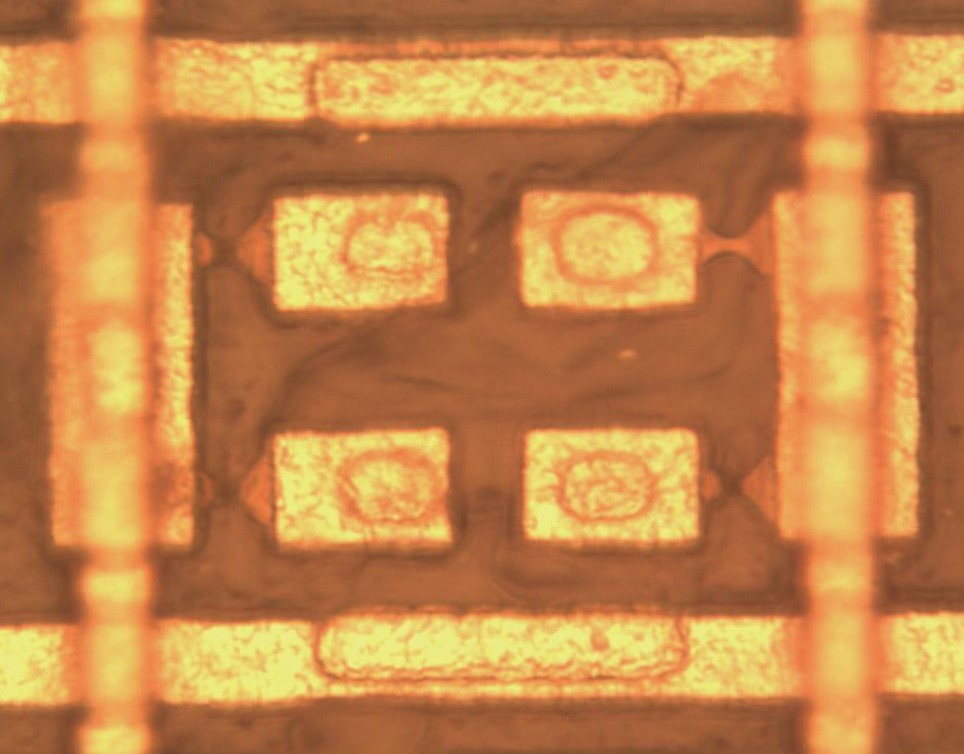
Example polysilicon fuses (National Semiconductor DMPAL16R):
Both the left and the bottom fuses are blown (non-conducting) but the upper right fuse is still conducting.
Anti-fuse
These are non-conductive until sufficient current flows through. See Wikipedia for details.
Seems like there's lots of kinds. Example pics:
http://klabs.org/richcontent/fpga_content/Antifuse_Data/b4/unprogrammed_m2m_antifuse_b4.jpg
http://klabs.org/richcontent/fpga_content/Antifuse_Data/b4/programmed_m2m_antifuse_b4.jpg
http://klabs.org/richcontent/fpga_content/pages/notes/antifuse_notes.htm